Fires can start in just a few seconds and when they do, every second matters. It could be a cooking accident, a faulty wire, or a small spark you didn’t even notice. Fires are unpredictable and dangerous. Sadly, many homes and businesses aren’t ready to handle them when they happen. There’s a common belief that having a smoke detector or being careful is enough. But when smoke fills a room or flames start to spread, what really makes the difference between safety and serious loss is often one thing: having a properly installed fire alarm system.
Fire alarm systems are built to catch signs of fire early and warn everyone in time. In this guide, you’ll learn how fire alarm systems work, the different types of fire alarm systems, how they’re installed, and what it takes to keep them running smoothly.
What Is a Fire Alarm System?
A fire alarm system is a group of connected devices that work together to detect fire and alert people nearby. These systems are designed to spot smoke, heat, or gas and then trigger alarms — both sound and lights to warn everyone quickly.
Unlike a basic smoke detector that only covers one room, a fire alarm system can cover an entire building and react automatically. It plays a key role in early warning, which gives people more time to leave safely and helps reduce damage. Whether it’s in a house, office, school, or warehouse, a fire alarm system is a crucial part of fire safety. It’s one of the simplest and most effective ways to lower risk and save lives.
How Does a Fire Alarm System Work?
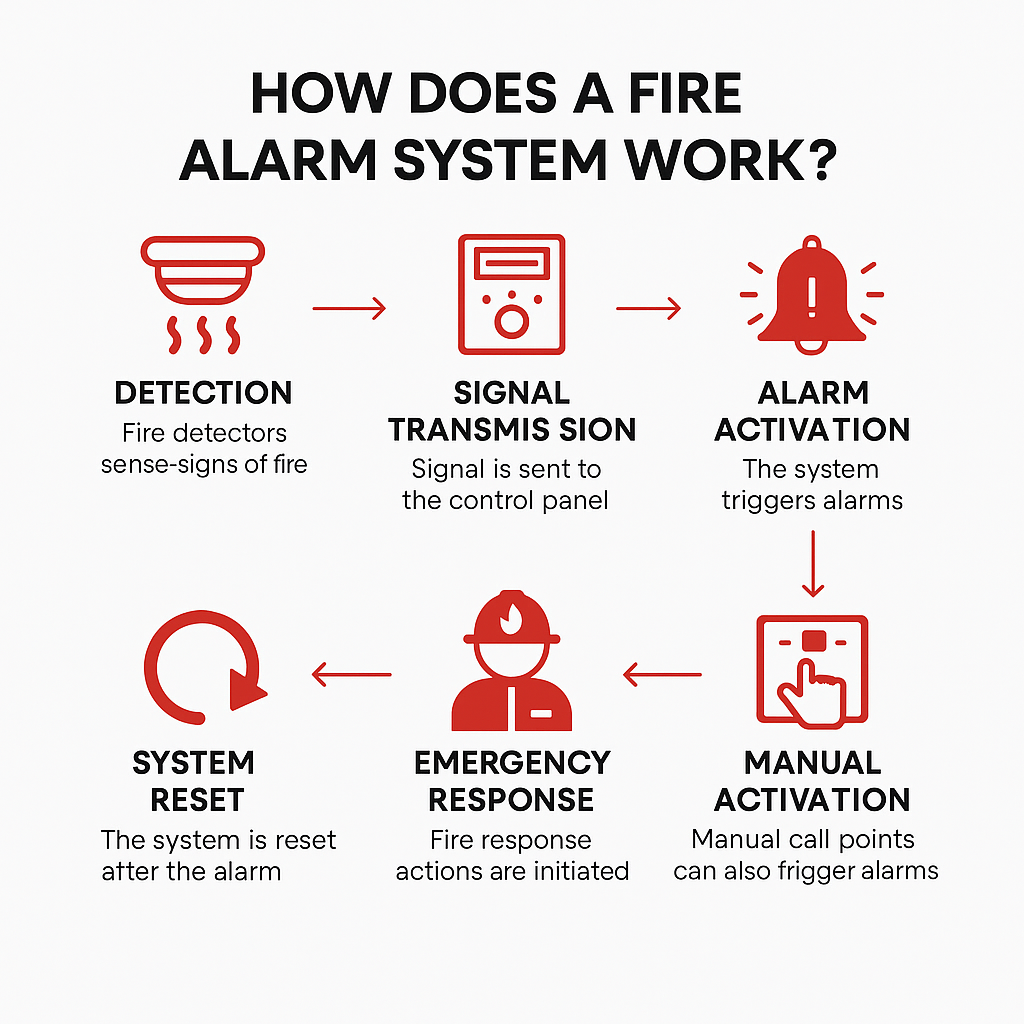
Fire alarm systems rely on a network of sensors and a central control panel to monitor the environment. Here’s how the process works from start to finish:
1. Detection
The first job of a fire alarm system is to detect the earliest signs of a fire. It does this using devices called fire detectors, which are installed throughout the building.
There are three common types:
- Smoke Detectors: These use either light sensors (photoelectric) or small electric currents (ionization) to detect smoke in the air. If smoke blocks the light or disrupts the current, the detector knows something is wrong.
- Heat Detectors: These react to a rise in temperature. Some are fixed-temperature (they go off at a set degree), while others measure how fast the temperature rises — both can signal a fire even without visible smoke.
- Gas Detectors: These are used in places where fires might release harmful gases like carbon monoxide. They trigger alarms if the gas level becomes unsafe.
These detectors work 24/7. The moment one senses danger, it sends a message to the next part of the system.
2. Signal Transmission
Once a detector spots danger, it sends a signal to the control panel. The control panel is basically the brain of the fire alarm system. It receives information from all the detectors and decides how to respond.
In simpler systems, the control panel can tell you which zone the signal came from. In more advanced setups, like addressable systems, it can show the exact location of the detector that was triggered. This helps responders know exactly where to go. The faster this signal is processed, the sooner people can be warned and action can be taken.
3. Alarm Activation
After the control panel confirms the danger, it turns on the alarm. This usually includes loud sirens or bells that can be heard throughout the building, plus flashing lights to make sure everyone sees the warning — even in noisy places or for people with hearing difficulties.
Some systems even include speakers that can give voice instructions, telling people which exits to use or what to do next. This alarm step is critical. It helps everyone react quickly, stay calm, and get out safely.
4. Manual Activation
Even though fire alarm systems work automatically, they also give people the power to sound the alarm themselves. In many buildings, you’ll see manual call points or break-glass units — little red boxes on the wall. If someone sees a fire or smells smoke before the detectors do, they can press the button or break the glass to set off the alarm right away.
This is a helpful backup, especially in places where a fire could start quickly or the detectors might take a little longer to pick it up.
5. Emergency Response
Once the alarm is sounding, everyone in the building should start evacuating. Meanwhile, the system may be doing other important things behind the scenes. It might close fire doors to stop flames from spreading, shut down elevators, or stop ventilation systems to keep smoke from moving through air ducts.
In many modern buildings, the fire alarm system is connected to a monitoring center or directly to the fire department. That means help can be on the way even if no one’s made a phone call yet. The whole point of this stage is to protect people, control the fire, and make sure emergency services are alerted as quickly as possible.
6. System Reset
After the fire is out or the danger turns out to be a false alarm, the system needs to be reset. This can only be done by someone authorized, like a building manager or trained technician.
First, they’ll check what caused the alarm. If it was dust, steam, or something else harmless, they’ll clean or fix the detector. If it was a real fire, they’ll make sure everything is safe before restarting the system. Once the control panel is reset, the system goes back to normal and keeps watching for any new danger.
 How Does a Fire Alarm System Get Activated?
How Does a Fire Alarm System Get Activated?
Fire alarm systems can be activated in two ways: automatically or manually.
In automatic activation, the system’s detectors pick up on smoke, heat, or gas that goes above a safe level. Once that happens, the system immediately turns on the alarm. This is the most common type of activation and is built into all modern systems.
Manual activation happens when a person uses a break-glass unit or call point to trigger the alarm. This might be necessary if someone sees flames before the detectors respond, or if the fire starts in a spot the system hasn’t covered yet.
Having both options ensures that no matter the situation, the system can do its job and alert everyone in time.
 Types of Fire Alarm Systems
Types of Fire Alarm Systems
Fire alarm systems come in different types, depending on the building’s size, layout, and specific safety needs. Choosing the right one makes a big difference in how quickly and accurately the system can respond.
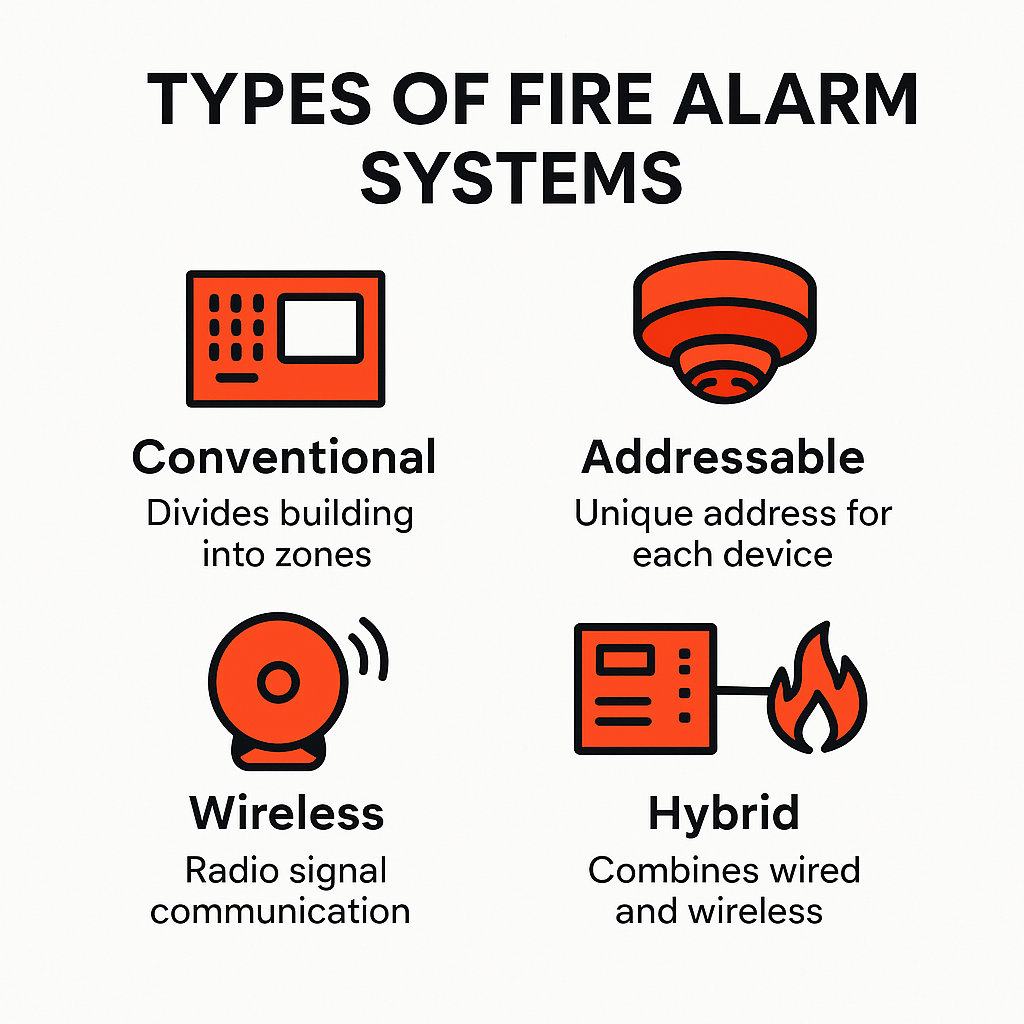
Conventional
Conventional fire alarm systems are often used in smaller buildings like homes, shops, or small offices. These systems divide the building into zones, and each zone is wired to a group of detectors connected to a control panel. If a detector in a zone is triggered, the control panel will show which zone it came from — but not the exact device. That means someone has to check the whole zone to find the source. While this takes a bit more time, conventional systems are reliable, affordable, and simple to install, which makes them a good choice for places with basic safety needs.
Addressable
Addressable systems take things a step further. Each device in the system — like smoke detectors or call points — has its own unique address. So, when one gets triggered, the control panel tells you exactly which device it was and where it’s located. This accuracy helps emergency teams respond faster and fix issues more easily. Addressable systems can also tell you if a detector is dirty or malfunctioning, which helps with maintenance. These systems are ideal for large buildings, hospitals, and places where fast, accurate response is essential.
Wireless
Wireless systems work just like addressable ones but without the need for wires. They use radio signals to connect the devices to the control panel. This makes installation easier, quicker, and less messy — especially in buildings where running wires is difficult or not allowed. Wireless systems are great for historic buildings, temporary setups, or renovations. They’re also flexible and easy to expand later. However, they do require careful setup to avoid signal problems, and they may cost a bit more upfront.
Hybrid
Hybrid systems combine both wired and wireless components. This allows for more flexibility, especially in buildings with mixed layouts. For example, you might use wired connections on the ground floor where access is easy and wireless devices in hard-to-reach upper levels or older sections. Hybrid systems are ideal for phased upgrades or expansions and allow property owners to modernize their fire safety without starting from scratch.
 Installing and Maintaining Fire Alarm Systems
Installing and Maintaining Fire Alarm Systems
Installing a fire alarm system isn’t as simple as placing a few devices on the wall. It starts with a proper risk assessment to understand the building’s layout and potential hazards. Then, you’ll need to choose the right system type, plan out where each detector goes, install the control panel with a backup power supply, and test everything to make sure it works.
After installation, regular maintenance is critical. Over time, dust and age can reduce the sensitivity of detectors. That’s why inspections, cleaning, and professional servicing should be done regularly to keep the system dependable. It’s not just about keeping it running — it’s about making sure it works when it really counts.
Conclusion
Fire alarm systems help detect danger early and warn people before a fire gets out of control. They use detectors, control panels, and alarms to keep buildings and people safe. From how they work to the types available and how to maintain them, it’s important to choose the right system for your space.
If you’re ready to take that step, explore cost-effective, certified fire alarm systems from Hac & Sons.


























 How Does a Fire Alarm System Get Activated?
How Does a Fire Alarm System Get Activated? Types of Fire Alarm Systems
Types of Fire Alarm Systems Installing and Maintaining Fire Alarm Systems
Installing and Maintaining Fire Alarm Systems





