Fire can happen anywhere. No area is completely safe, not even factories, warehouses, offices, kitchens, or construction sites. When chemicals, combustible materials, or heavy machines are involved, the danger goes up. That’s why every commercial or industrial building has to have the necessary fire fighting tools for putting out fires to keep people safe, protect them, and respond quickly.
This blog will show you the top five tools that any business should have to keep fire safety up to par.
Why Industrial Fire Safety Matters
Fires do more than only damage things. They disturb work, endanger lives, and can lead to major legal and financial losses. Most industrial fires are caused by things that might have been avoided, such bad wiring, leaking chemicals, machinery that get too hot, or simply carelessness.
But even when safety is the first priority, accidents can still happen. If you have the correct fire safety equipment on hand, your employees can respond fast, put out the fire, and lower the chance of injury or damage before aid comes.
Let’s take a look at the best firefighting tools that every industry needs.
 1. Fire Extinguishers
1. Fire Extinguishers
Fire extinguishers are the first thing that people use to put out a fire. They are small, simple to operate, and quite effective when utilised properly.
But not all fire extinguishers are the same. There are numerous kinds of fire extinguishers for different sorts of fires:
- Class A: Plastic, wood, and paper
- Class B: Liquids that can catch fire, such fuel and oil
- Class C: Fires caused by electricity
- Class D: Metals
- Class K: oils and fats used in cooking
When there are fire hazards in an industrial setting, it’s crucial to pick the correct sort of extinguisher. A chemical industry could need a foam or dry powder extinguisher, but a data centre should have CO2 extinguishers that don’t leave any trace.
A lot of businesses make the error of making use of only one type in the whole building. This might be harmful. A good fire risk assessment can help you figure out what kinds of extinguishers you need to put in place.

2. Fire Hose Reels
When a fire gets too big for an extinguisher to handle, that’s where fire hose reels come in. They’re hooked up to a steady water supply and give you a long, flexible hose that lets water flow nonstop, making it easier to control bigger fires.
They are meant to be used by qualified people and are good at cooling down high-temperature fires quickly. Fire hose reels can be helpful in places with high heat sources, big open floors, or areas full with machinery.
Hose reels are useful because they can reach a long way. A hose reel can cover more space than an extinguisher, which only works up close. It also never runs out of water as long as the supply is stable.
Also Read: Why Every Commercial Building Should Have A Fire Hose Reel
 3. Fire Blankets
3. Fire Blankets
A fire blanket might seem basic, but it can be a real lifesaver in an emergency. These are made from flame-resistant materials like fiberglass, it works by quickly covering small fires and cutting off their oxygen supply, putting them out fast and safely
They are very helpful in:
- Kitchens or food processing areas
- Electrical panels
- Small chemical spills
- Emergencies where a person is on fire
Fire blankets should be close to workstations in industries that use flammable chemicals or do jobs that need a lot of heat. They’re also helpful for covering persons whose garments catch fire, which gives them short protection until aid comes.
Fire blankets don’t cause any mess or residue, which makes clean up easier as compared to fire extinguishers.
 4. Fire and Smoke Detectors
4. Fire and Smoke Detectors
Early detection is the first step in prevention. People in factories typically don’t pay attention to fire and smoke alarms, yet they may warn workers of danger before the fires even start. These detectors emit alarms to tell everyone to respond quickly when they detect smoke, heat, or gas in the air.
There are many kinds of detectors:
- Ionization smoke detectors: Better for fast-flaming fires
- Photoelectric smoke detectors: Better for slow, smoldering fires
- Heat detectors: Triggered by rapid rise in temperature
- Gas leak detectors: Detect presence of gases like LPG, methane, or CO
Placing detectors throughout an industrial site helps catch issues early, especially in areas like storage rooms, chemical zones, or maintenance areas. These detectors are usually connected to alarms and emergency exits, which makes it easier and faster for people to evacuate when needed.
Also Read: How Fire Alarm Systems Work: A Complete Guide
 5. Fire Hydrant System
5. Fire Hydrant System
One of the best firefighting tools for tackling fires on site is a fire hydrant system. It sends a continuous stream of water straight to the hoses that the building’s internal crew or emergency fire brigades utilise. Hydrants are very important for quick reaction in industries with big regions or a lot of fire.
These are usually set up outside and linked to water tanks, overhead tanks, or the main city water lines. In larger buildings, you’ll also find some installed indoors, often placed near staircases or service areas for quick access.
What makes them important is scale and pressure. Fire hydrants can tackle large-scale fires that ordinary extinguishers or hose reels can’t handle. While they require more training to operate, they’re often life-saving during serious incidents.
Some businesses assume hydrants are only for firefighters, but trained in-house staff can also use them during the early minutes of a fire.
Bonus Safety Essentials to Support Fire Fighting Tools
While tools are critical, they must be supported by good planning and staff awareness. Here are a few elements that complete the picture:
- Fire escape plans clearly marked in the workplace
- Emergency lighting to guide people during blackouts
- Fireproof cabinets for storing chemicals or documents
- Signage that identifies equipment and escape routes
Tools alone don’t guarantee safety. People must know how to use them and where they are stored. Keeping them maintained and tested regularly also matters.
Common Mistakes Industries Make with Fire Safety
Some businesses treat fire fighting tools as a one-time investment. They install extinguishers and forget about them. But fire safety is an ongoing process. Some common mistakes include:
- Not checking expiry dates on extinguishers
- Blocking access to tools or exits
- Using the wrong type of extinguisher
- Failing to test alarm systems regularly
These issues can cause delay or failure during real emergencies. A fire can spread in seconds, so every second matters.
Final Thoughts
Not only do the industries require good machines or trained staff, they also need a full fire safety system. The right fire fighting tools, placed correctly and maintained properly, can prevent disasters and protect both people and property.
Need Quality Fire Safety Equipment for Your Industry?
At HAC & Sons, we supply tested, certified, and durable fire safety tools for all industries. From extinguishers and hose reels to detectors and hydrant systems, we’ve got the essentials you need to stay prepared.
Contact us today to upgrade your fire safety setup or speak with an expert. We help you stay ready, every day.



































 Why Fire Ball Extinguishers Matter
Why Fire Ball Extinguishers Matter Long-Lasting Benefits of Fire Ball Extinguishers
Long-Lasting Benefits of Fire Ball Extinguishers
 Why Quick Action Matters
Why Quick Action Matters Choosing the Right Fire Hose Reel
Choosing the Right Fire Hose Reel

 Which One’s Better?
Which One’s Better?
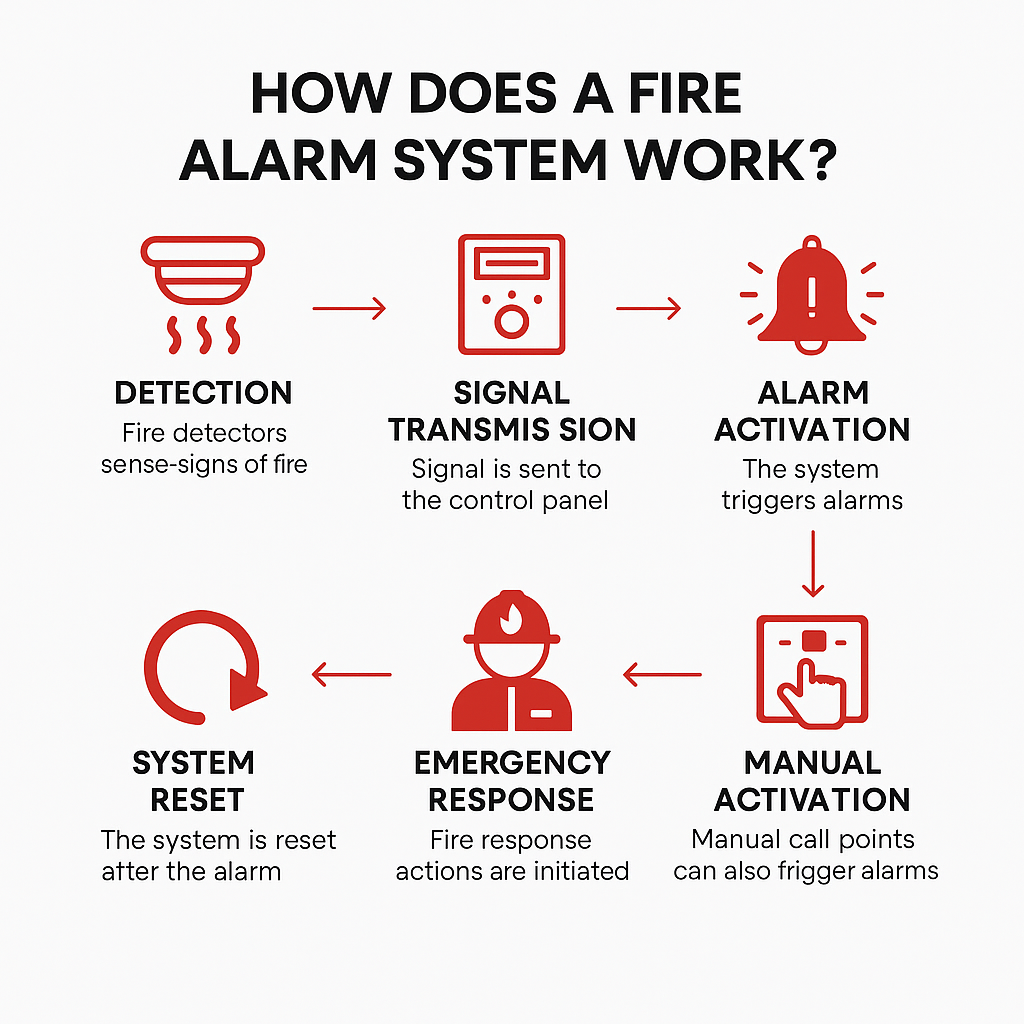 How Does a Fire Alarm System Get Activated?
How Does a Fire Alarm System Get Activated? Types of Fire Alarm Systems
Types of Fire Alarm Systems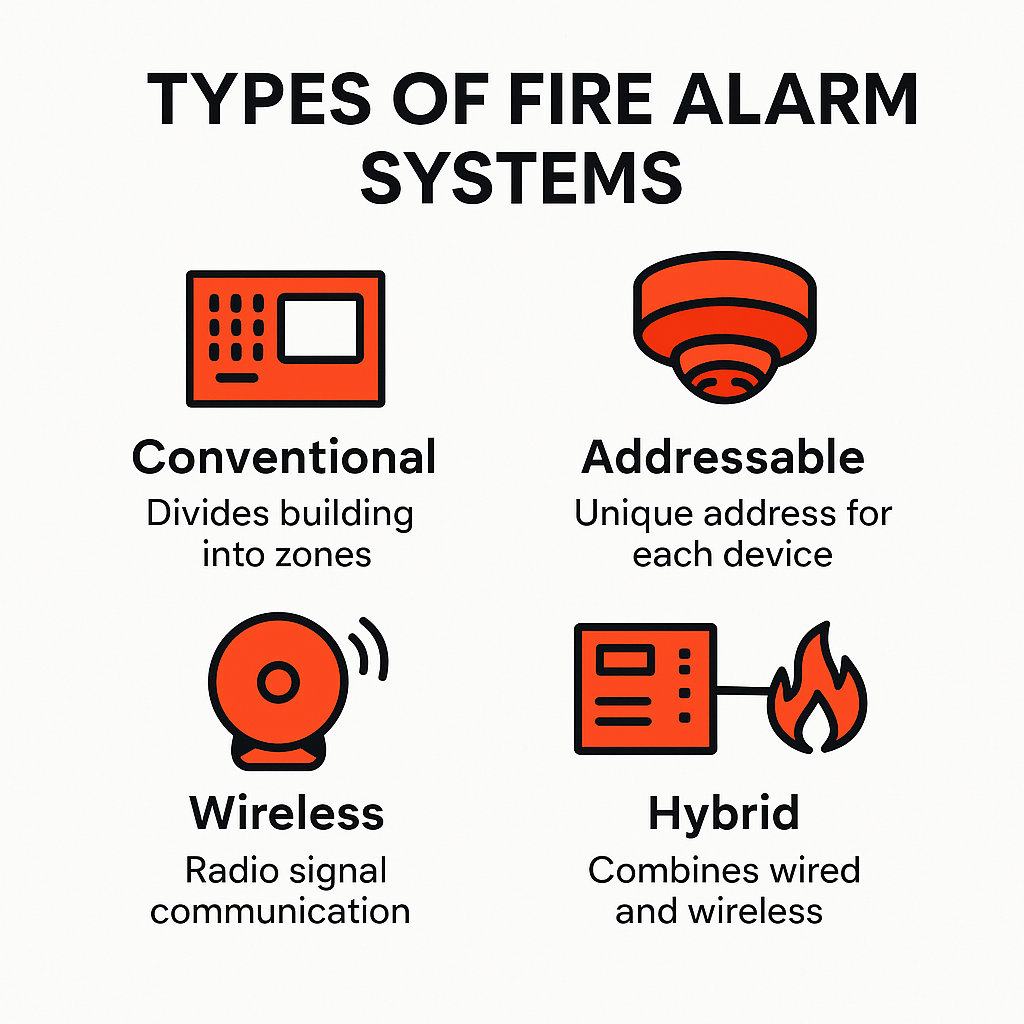 Installing and Maintaining Fire Alarm Systems
Installing and Maintaining Fire Alarm Systems